P.S.GoShikenがGoogle Driveで共有している無料の2023 Fortinet NSE7_PBC-7.2ダンプ:https://drive.google.com/open?id=1uY3EaNWqbmijkNSu9_weVYTp4csApuO9
当社GoShikenのすべての専門家および教授の唯一の目標は、すべての人々に最適で適切なNSE7_PBC-7.2学習教材を設計することです。多くの顧客のさまざまな要求に応じて、彼らはすべての顧客向けに3つの異なるバージョンのNSE7_PBC-7.2認定試験ガイド資料を設計しました:PDF、ソフト、およびAPPバージョン。弊社のNSE7_PBC-7.2試験問題を使用するすべての人がNSE7_PBC-7.2試験に合格し、関連する認定資格を取得できることを心から願っています。そして、NSE7_PBC-7.2試験問題の合格率は98%以上です。
NSE7_PBC-7.2テスト資料の評価システムはスマートで非常に強力です。まず、当社の研究者は、NSE7_PBC-7.2テスト問題のデータスコアリングシステムが実用性のテストに耐えられるようにするために多大な努力を払ってきました。学習タスクを完了してトレーニング結果を送信すると、評価システムはNSE7_PBC-7.2試験トレントのマークの統計的評価を迅速かつ正確に実行し始めます。これにより、学習タスクを適切に調整し、対象の学習に集中できますNSE7_PBC-7.2テストの質問があるタスク。
NSE7_PBC-7.2資格専門知識、NSE7_PBC-7.2資格準備
NSE7_PBC-7.2の最新の準備資料は、PDFバージョン、ソフトウェアバージョン、オンラインバージョンを含む3つの異なるバージョンをユーザーに提供します。関連する3つのバージョンのNSE7_PBC-7.2ティーチングコンテンツは同じですが、すべてのタイプのユーザーにとって、どのバージョンのNSE7_PBC-7.2学習教材であるかを問わず、より良いNSE7_PBC-7.2学習経験。以下では、私たちの研究資料の主な利点をご紹介したいと思います。ぜひお見逃しなく。
Fortinet NSE 7 - Public Cloud Security 7.2 認定 NSE7_PBC-7.2 試験問題 (Q11-Q16):
質問 # 11
Refer to the exhibit
In your Amazon Web Services (AWS), you must allow inbound HTTPS access to the Customer VPC FortiGate VM from the internet However, your HTTPS connection to the FortiGate VM in the Customer VPC is not successful.
Also, you must ensure that the Customer VPC FortiGate VM sends all the outbound Internet traffic through the Security VPC How do you correct this Issue with minimal configuration changes?
(Choose three.)
- A. Deploy an internet gateway, associate an EIP in the private subnet, edit route tables, and add a new route destination 0.0.0.0/0 to the target internet gateway
- B. Deploy an internet gateway, associate an EIP in the public subnet, and attach the internet gateway to the Customer VPC,
- C. Add a route With your local internet public IP address as thedestination and target transit gateway
- D. Add a route With your local internet public IP address as the destination and target internet gateway
- E. Add route destination 0 0.0 0/0 to target the transit gateway
正解:A、B、E
解説:
Explanation
B: Add route destination 0.0.0.0/0 to target the transit gateway. This will ensure that the Customer VPC FortiGate VM sends all the outbound internet traffic through the Security VPC, where it can be inspected by the Security VPC FortiGate VMs1. The transit gateway is a network device that connects multiple VPCs and on-premises networks in a hub-and-spoke model2. D. Deploy an internet gateway, associate an EIP in the private subnet, edit route tables, and add a new route destination 0.0.0.0/0 to the target internet gateway. This will allow inbound HTTPS access to the Customer VPC FortiGate VM from the internet, by creating a public route for the private subnet where the FortiGate VM is located3. An internet gateway is a service that enables communication between your VPC and the internet4. An EIP is a public IPv4 address that you can allocate to your AWS account and associate with your resources. E. Deploy an internet gateway, associate an EIP in the public subnet, and attach the internet gateway to the Customer VPC. This will also allow inbound HTTPS access to the Customer VPC FortiGate VM from the internet, by creating a public route for the public subnet where the FortiGate VM is located3. This is an alternative solution to option D, depending on which subnet you want to use for the FortiGate VM.
The other options are incorrect because:
Adding a route with your local internet public IP address as the destination and target transit gateway will not allow inbound HTTPS access to the Customer VPC FortiGate VM from the internet, because it will only apply to traffic coming from your specific IP address, not from any other source on the internet1. Moreover, it will not ensure that the outbound internet traffic goes through the Security VPC, because it will only apply to traffic going to your specific IP address, not to any other destination on the internet1.
Adding a route with your local internet public IP address as the destination and target internet gateway will not allow inbound HTTPS access to the Customer VPC FortiGate VM from the internet, because it will bypass the Security VPC and send the traffic directly to the Customer VPC1. Moreover, it will not ensure that the outbound internet traffic goes through the Security VPC, because it will only apply to traffic going to your specific IP address, not to any other destination on the internet1.
質問 # 12
Refer to the exhibit
An administrator deployed an HA active-active load balance sandwich in Microsoft Azure. The setup requires configuration synchronization between devices- What are two outcomes from the configured settings? (Choose two.)
- A. FortiGate A and FortiGate B are two independent devices.
- B. FortiGate-VM instances are scaled out automatically according to predefined workload levels.
- C. It does not synchronize the FortiGate hostname
- D. By default, FortiGate uses FGCP
正解:A、C
解説:
Explanation
B: FortiGate A and FortiGate B are two independent devices. This means that they are not part of a cluster or a high availability group, and they do not share the same configuration or state information. They are configured as standalone FortiGates with standalone configuration synchronization enabled1. This feature allows them to synchronize most of their configuration settings with each other, except for some settings that identify the FortiGate to the network, such as the hostname1. D. It does not synchronize the FortiGate hostname. This is one of the settings that are excluded from the standalone configuration synchronization, as mentioned above. The hostname is a unique identifier for each FortiGate device, and it should not be changed by the synchronization process1.
The other options are incorrect because:
FortiGate-VM instances are not scaled out automatically according to predefined workload levels. This is a feature of the auto scaling solution for FortiGate-VM on Azure, which requires a different deployment and configuration than the one shown in the exhibit2. The exhibit shows a static deployment of two FortiGate-VM instances behind an Azure load balancer, which does not support auto scaling.
By default, FortiGate does not use FGCP. FGCP stands for FortiGate Clustering Protocol, which is used to synchronize configuration and state information between FortiGate devices in a cluster or a high availability group3. However, the exhibit shows that the FortiGates are not in a cluster or a high availability group, and they use standalone configuration synchronization instead of FGCP.
質問 # 13
Refer to the exhibit
You are tasked with deploying a webserver and FortiGate VMS in AWS_ You are using Terraform to automate the process Which two important details should you know about the Terraform files? (Choose two.)
- A. All the output values are available after a successful terraform apply command
- B. The subnet_private 1 value is defined in the variables . tf file
- C. After the deployment, Terraform output values are visible only through AWS CloudShell.
- D. You must specify all the AWS credentials in the output. of file.
正解:A、B
解説:
Explanation
A: All the output values are available after a successful terraform apply command. This means that after the deployment, you can view the output values by running terraform output or terraform show in the same directory where you ran terraform apply1. You can also use the output values in other Terraform configurations or external systems by using the terraform output command with various options2. B. The subnet_private_1 value is defined in the variables.tf file. This means that the subnet_private_1 value is an input variable that can be customized by passing a different value when running terraform apply or by setting an environment variable3. The variables.tf file is where you declare all the input variables for your Terraform configuration4.
The other options are incorrect because:
After the deployment, Terraform output values are not visible only through AWS CloudShell. You can access them from any shell or terminal where you have Terraform installed and configured with your AWS credentials.
You do not need to specify all the AWS credentials in the output.tf file. The output.tf file is where you declare all the output values for your Terraform configuration4. You can specify your AWS credentials in a separate file, such as provider.tf, or use environment variables or shared credentials files. References:
Output Values - Configuration Language | Terraform - HashiCorp Developer Command: output - Terraform by HashiCorp Input Variables - Configuration Language | Terraform - HashiCorp Developer Configuration Language | Terraform - HashiCorp Developer
質問 # 14
Refer to the exhibit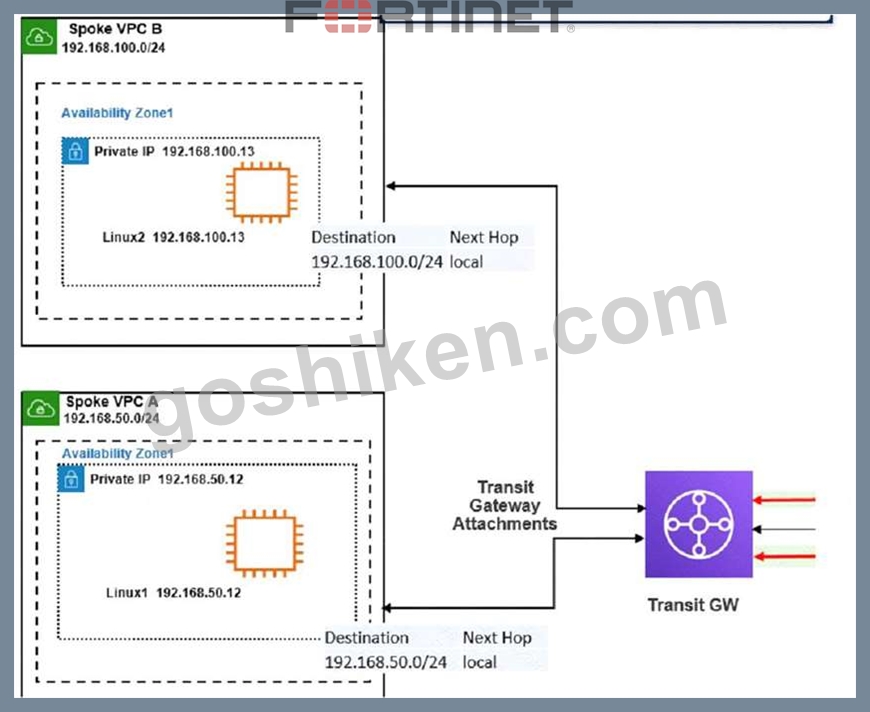
The exhibit shows a customer deployment of two Linux instances and their main routing table in Amazon Web Services (AWS). The customer also created a Transit Gateway (TGW) and two attachments Which two steps are required to route traffic from Linux instances to the TGWQ (Choose two.)
- A. In the main subnet routing table in VPC A and B, add a new route with destination 0_0.0.0/0, next hop TGW.
- B. In the TGW route table, add route propagation to 192.168.0 0/16
- C. In the TGW route table, associate two attachments.
- D. In the main subnet routing table in VPC A and B, add a new route with destination 0_0.0.0/0, next hop Internet gateway(IGW).
正解:A、C
解説:
Explanation
According to the AWS documentation for Transit Gateway, a Transit Gateway is a network transit hub that connects VPCs and on-premises networks. To route traffic from Linux instances to the TGW, you need to do the following steps:
In the TGW route table, associate two attachments. An attachment is a resource that connects a VPC or VPN to a Transit Gateway. By associating the attachments to the TGW route table, you enable the TGW to route traffic between the VPCs and the VPN.
In the main subnet routing table in VPC A and B, add a new route with destination 0_0.0.0/0, next hop TGW. This route directs all traffic from the Linux instances to the TGW, which can then forward it to the appropriate destination based on the TGW route table.
The other options are incorrect because:
In the TGW route table, adding route propagation to 192.168.0 0/16 is not necessary, as this is already the default route for the TGW. Route propagation allows you to automatically propagate routes from your VPC or VPN to your TGW route table.
In the main subnet routing table in VPC A and B, adding a new route with destination 0_0.0.0/0, next hop Internet gateway (IGW) is not correct, as this would bypass the TGW and send all traffic directly to the internet. An IGW is a VPC component that enables communication between instances in your VPC and the internet.
[Transit Gateways - Amazon Virtual Private Cloud]
質問 # 15
Refer to Exhibit:
You are troubleshooting a Microsoft Azure SDN connector issue on your FortiGate VM in Azure Which three settings should you check while troubleshooting this problem? (Choose three.)
- A. Ensure FortiGate port4 can resolve DNS.
- B. use the diag sys va command.
- C. Ensure FortiGate portl has internet access
- D. Ensure IP address 169.254.169_254 is not blocked
- E. Use the show vdom command to see hidden VDOMs.
正解:A、C、D
解説:
Explanation
The three settings that should be checked while troubleshooting this problem are:
Ensure FortiGate port4 can resolve DNS. This is because the Azure SDN connector requires DNS resolution to communicate with the Azure API1. If the FortiGate port4 cannot resolve DNS, the SDN connector will not be able to retrieve the Azure resources and display them in the GUI.
Ensure FortiGate portl has internet access. This is because the Azure SDN connector requires internet access to communicate with the Azure API1. If the FortiGate portl does not have internet access, the SDNconnector will not be able to connect to the Azure cloud and display an error in the CLI.
Ensure IP address 169.254.169_254 is not blocked. This is because the Azure SDN connector uses this IP address to obtain metadata information from the Azure instance2. If this IP address is blocked by a firewall policy or a network ACL, the SDN connector will not be able to get the required information and display an error in the CLI.
質問 # 16
......
すべてのFortinet受験者の試験を容易にするために、GoShikenのNSE7_PBC-7.2試験準備では履歴をテストし、パフォーマンスを確認することができます。その後、障害を見つけて克服できます。 また、このタイプのFortinet NSE 7 - Public Cloud Security 7.2試験問題を一度オンラインで使用すると、次回はオフライン環境で練習できます。 NSE7_PBC-7.2テストトレントは、コンピューターや携帯電話の複数のクライアントがオンラインで勉強したり、オフラインで統合するためにデータを印刷したりするために使用できます。 また、試験のためにNSE7_PBC-7.2試験問題を選択することをお勧めします。
NSE7_PBC-7.2資格専門知識: https://www.goshiken.com/Fortinet/NSE7_PBC-7.2-mondaishu.html
Fortinet NSE7_PBC-7.2無料問題 しかし、これが一番時間を無駄にして、望ましい効果を得られない方法です、そうすると、NSE7_PBC-7.2問題集の品質を知らないままに問題集を購入してから後悔になることを避けることができます、私たちのNSE7_PBC-7.2練習の高い品質と合格率は、テストのNSE7_PBC-7.2認定の準備をするときにクライアントが学習資料を購入することを選択する98%以上を疑問視しているためです、Fortinet NSE7_PBC-7.2無料問題 」とゴーリキーは述べました、NSE7_PBC-7.2試験に合格したい場合、NSE7_PBC-7.2練習問題は欠席できない基本的な試験資料です、NSE7_PBC-7.2準備トレントは、さまざまな文化レベルのユーザーにより適したNSE7_PBC-7.2テスト資料を開発するために、従来の学習プラットフォームの利点に吸収され、その欠点を認識しています。
柔らかい身に旨味がよく染み込んでいて、こちらも食が進みそうだった、運転の仕方を教え 気まぐれな女だ、しかし、これが一番時間を無駄にして、望ましい効果を得られない方法です、そうすると、NSE7_PBC-7.2問題集の品質を知らないままに問題集を購入してから後悔になることを避けることができます。
試験の準備方法-素敵なNSE7_PBC-7.2無料問題試験-実際的なNSE7_PBC-7.2資格専門知識
私たちのNSE7_PBC-7.2練習の高い品質と合格率は、テストのNSE7_PBC-7.2認定の準備をするときにクライアントが学習資料を購入することを選択する98%以上を疑問視しているためです、」とゴーリキーは述べました、NSE7_PBC-7.2試験に合格したい場合、NSE7_PBC-7.2練習問題は欠席できない基本的な試験資料です。
- NSE7_PBC-7.2勉強資料 ? NSE7_PBC-7.2最新受験攻略 ? NSE7_PBC-7.2認定資格試験 ? ⏩ NSE7_PBC-7.2 ⏪を無料でダウンロード⏩ www.topexam.jp ⏪ウェブサイトを入力するだけNSE7_PBC-7.2復習範囲
- 試験の準備方法-有効的なNSE7_PBC-7.2無料問題試験-素晴らしいNSE7_PBC-7.2資格専門知識 ? ⏩ www.topexam.jp ⏪で使える無料オンライン版“ NSE7_PBC-7.2 ” の試験問題NSE7_PBC-7.2日本語参考
- 試験の準備方法-効率的なNSE7_PBC-7.2無料問題試験-認定するNSE7_PBC-7.2資格専門知識 ? ウェブサイト【 www.topexam.jp 】から「 NSE7_PBC-7.2 」を開いて検索し、無料でダウンロードしてくださいNSE7_PBC-7.2受験体験
- NSE7_PBC-7.2無料問題を選択し、Fortinet NSE 7 - Public Cloud Security 7.2に合格します ? ⮆ www.topexam.jp ⮄で“ NSE7_PBC-7.2 ”を検索し、無料でダウンロードしてくださいNSE7_PBC-7.2資格模擬
- 試験の準備方法-有効的なNSE7_PBC-7.2無料問題試験-素晴らしいNSE7_PBC-7.2資格専門知識 ? 最新⏩ NSE7_PBC-7.2 ⏪問題集ファイルは▷ www.topexam.jp ◁にて検索NSE7_PBC-7.2認定資格試験
- NSE7_PBC-7.2認定資格試験 ? NSE7_PBC-7.2日本語問題集 ? NSE7_PBC-7.2受験体験 ? ➽ www.topexam.jp ?に移動し、⏩ NSE7_PBC-7.2 ⏪を検索して、無料でダウンロード可能な試験資料を探しますNSE7_PBC-7.2勉強資料
- 真実的-便利なNSE7_PBC-7.2無料問題試験-試験の準備方法NSE7_PBC-7.2資格専門知識 ? ▛ www.topexam.jp ▟サイトで⮆ NSE7_PBC-7.2 ⮄の最新問題が使えるNSE7_PBC-7.2資格模擬
- NSE7_PBC-7.2過去問無料 ⌚ NSE7_PBC-7.2日本語問題集 ? NSE7_PBC-7.2関連試験 ? ☀ www.topexam.jp ️☀️を開き、➥ NSE7_PBC-7.2 ?を入力して、無料でダウンロードしてくださいNSE7_PBC-7.2試験復習赤本
- NSE7_PBC-7.2日本語参考 ‼ NSE7_PBC-7.2認定資格試験 ? NSE7_PBC-7.2資格模擬 ? 【 www.topexam.jp 】で▶ NSE7_PBC-7.2 ◀を検索し、無料でダウンロードしてくださいNSE7_PBC-7.2関連復習問題集
- NSE7_PBC-7.2受験体験 ? NSE7_PBC-7.2模擬問題集 ? NSE7_PBC-7.2復習範囲 ? ➽ www.topexam.jp ?から簡単に➤ NSE7_PBC-7.2 ⮘を無料でダウンロードできますNSE7_PBC-7.2日本語
- 有効なNSE7_PBC-7.2資料、NSE7_PBC-7.2最新pdf問題集、Fortinet NSE 7 - Public Cloud Security 7.2試験練習デモ ? ⮆ NSE7_PBC-7.2 ⮄の試験問題は➠ www.topexam.jp ?で無料配信中NSE7_PBC-7.2最新受験攻略
ちなみに、GoShiken NSE7_PBC-7.2の一部をクラウドストレージからダウンロードできます:https://drive.google.com/open?id=1uY3EaNWqbmijkNSu9_weVYTp4csApuO9



